Diabetes is one of the dreadful diseases which can cause irreversible damage to the eye sight. It is very common cause of blindness esp. in western countries & now a day also in India. People with untreated diabetes are said to be 25 times more at risk for blindness than the general population.
The extent & severity of damage depends on duration of diabetes (i.e. since how many years the patient is suffering from the disease) and the control of the disease. About 80% of the people who have had diabetes for at least 15 years have some blood vessel damage to their retina. People with juvenile diabetes are more likely to develop diabetic retinopathy at a younger age.
From the variety of systemic problems like heart disease, kidney disease caused by diabetes, it also enhances the risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma.
HOW DOES IT DAMAGE THE EYE ?
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that is
caused by changes in the blood vessels in the eye. High
Blood sugar and other abnormalities in the metabolism may
damage the blood vessels which lead to decreased oxygen
supply and damage to retina in the eye. Theses small blood
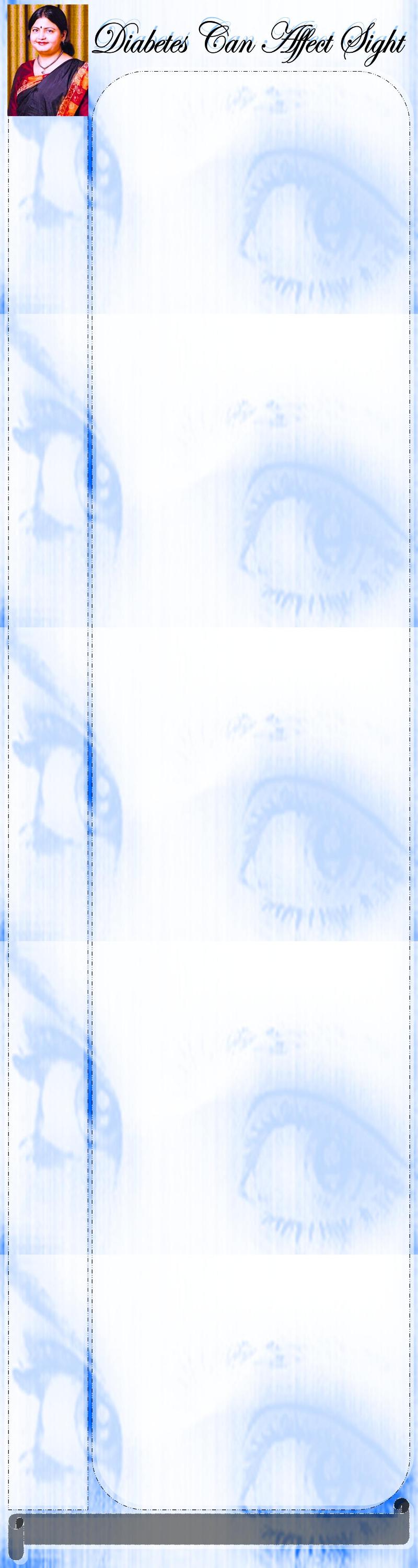
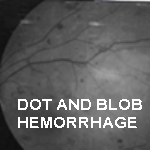
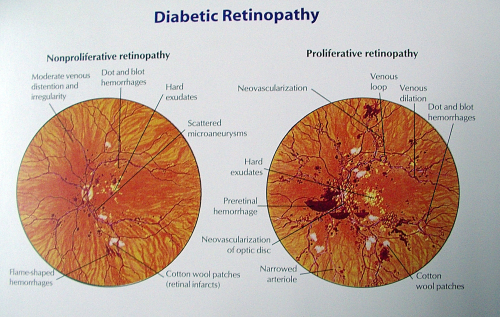
vessels begin to balloon-causing micro aneurysms and leak
fluid called edema or leak blood called dot and blob
hemorrhages. This phase is known as Background Diabetic
Retinopathy or nonproliferative diabetic Retinopathy.
If the fluid accumulates in macular region (central part
of retina) it is known as diabetic macular edema.
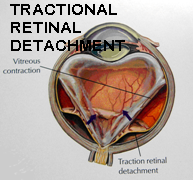
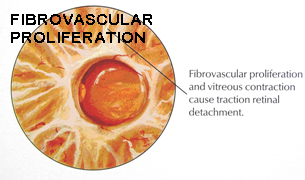
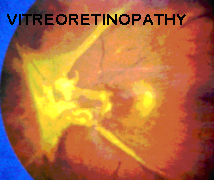
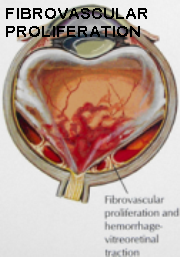
As a response to less oxygen supply to retina, new blood vessels begin to grow which are extremely leaky and fragile and much more harmful. They on slightest insult or injury bleed inside the eye causing vitreous hemorrhage. This hemorrhage may absorb within 3 months or else may cause fibrosis resulting into scarring and thereby tract ional retinal detachment. This causes permanent visual loss.
In the process the new blood vessels in the retina, it also grows on the iris surface and trabecular meshwork causing hindrance to the aqueous outflow and thereby causing glaucoma.
SYMPTOMS - DEPENDING ON SEVERITY AND AGE OF DIABETES
- No Symptoms
- Gradual blurring of vision
- Detected on Routine medical examination
- Hazy vision
- Complete loss of vision
HOW IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DIAGNOSED ?
Thorough examination of the eyes by doing fundoscopy with ophthalmoscope after dilating the pupils with mydriatric drops is must. At times, Fluorescein Angiography whereby dye is injected in your arm and special photos are taken is necessary.
WHEN TO SEEK ADVICE ?
In order to avoid sight threatening complications, one should have his eyes examined every 1 year after the diabetes is first detected, and thereby according the advice of the eye physician.
HOW IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY TREATED ?
According to the stage of diabetic retinopathy,
the treatment differs. At times only regular
follow up apart from any treatment is necessary.
-
Laser Surgery :- Small bursts of laser
beams in order to seal the leaking of
the blood vessels = photocoagulation is
done in outpatient department only.
-
Vitrectomy :- Vitrectomy is done in
late cases where the leaked blood
in the vitreous is removed and
clear solution is replaced in the
operation theatre.
-
Retinal detachment repair :-
Surgery is done to release the
traction and the retina is
reattached.
- Cryotherapy :- In late stages in
order to decrease the pain and for
shrinking the blood vessels
Cryotherapy= freezing is done.
HOW CAN THE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY -
VISION LOSS BE PREVENTED ?
- Early detection
- Monitoring of blood sugar levels regularly
- Proper control of diabetes as per
physician’s advice - Attitude towards medications and diet
- Physical activity/ Regular exercise
- Regular checkups with eye physician
- Proper knowledge of the complications
- Avoiding smoking and drinking in moderation
- Healthy eating
Commitment for the avoidance of complications is
needed from both sides- patients and doctor.